Using column generation in constraint-and-column generation for adjustable robust optimization > GAP
Loading the data
Our results can be found in the results.gap.csv file
with the following columns:
- “tag”: a tag always equal to “result” used grep the result line in our execution log file.
- “instance”: the path to the instance.
- “standard_phase_time_limit”: the time limit for the standard phase (i.e., without using CG).
- “master_solver”: the solver used for solving the CCG master problem: STD for standard, i.e., Gurobi, CG for column generation.
- “status”: the final status.
- “reason”: the final status reason.
- “has_large_scaled”: true if the CG phase has been started, false otherwise.
- “n_iterations”: the number of iterations.
- “total_time”: the total time to solve the problem.
- “master_time”: the time spent solving the master problem.
- “adversarial_time”: the time spent solving the adversarial problem.
- “best_bound”: the best bound found.
- “best_obj”: the best feasible point value.
- “relative_gap”: the final relative gap.
- “absolute_gap”: the final absolute gap.
- “adversarial_unexpected_status”: the status of the adversarial problem solver if it is not Optimal.
- “with_heuristic”: true if the CG-based heuristic is used.
- “n_facilities”: the number of facilities in the instance.
- “n_customers”: the number of customers in the instance.
- “Gamma”: the value for the uncertainty budget \(\Gamma\).
- “blank”: this column is left blank.
data = read.csv("results.csv", header = FALSE)
colnames(data) = c("slurm_file", "tag", "instance", "with_heuristic", "n_facilities", "n_customers", "Gamma", "standard_phase_time_limit", "master_solver", "status", "reason", "has_large_scaled", "n_iterations", "total_time", "master_time", "adversarial_time", "best_bound", "best_obj", "relative_gap", "absolute_gap", "second_stage.mean", "second_stage.std_dev", "adversarial_unexpected_status", "memory_used", "memory_limit")For homogeneity, we fix the total_time of unsolved instances to the time limit.
if (sum(data$tag == "iteration") > 0 ) {
data[data$tag == "iteration",]$total_time = 10800
}
if (sum(data$total_time > 10800) > 0 ) {
data[data$total_time > 10800,]$total_time = 10800
}We start by removing the “tag” and the “blank” columns.
#data$tag = NULL
data$slurm_file = NULLThen, we create a column named “method” which gives a specific name to each method, comprising the approach for solving the CCG master problem, the time limit of the standard phase and a flag indicating if the CG-based heuristic was used.
data$method = paste0(data$master_solver, "_TL", data$standard_phase_time_limit, "_H", data$with_heuristic)
unique(data$method)## [1] "CG_TL0_H0" "CG_TL0_H1" "STD_TLInf_H0"Our final data reads.
Sanity Check
# Define the relative tolerance
tolerance <- 10^-2
# Filter the data where time < 10800 and group by 'instance'
validation <- data %>%
filter(total_time < 10800) %>%
group_by(paste0(instance, "_", Gamma)) %>%
summarise(min_best_obj = min(best_obj), max_best_obj = max(best_obj)) %>%
mutate(valid = (max_best_obj - min_best_obj) / min_best_obj <= tolerance)
# Check if all instances are valid
if (all(validation$valid)) {
print("All methods find the same best_obj value within the relative tolerance for all instances.")
} else {
print("Methods do not find the same best_obj value within the relative tolerance for some instances.")
print(validation %>% filter(!valid)) # Show the instances that failed validation
}## [1] "All methods find the same best_obj value within the relative tolerance for all instances."Empirical Cumulative Distribution Function (ECDF)
We plot the ECDF of computation time over our set of instances for all approaches.
ggplot(data, aes(x = total_time, col = method)) + stat_ecdf(pad = FALSE) +
coord_cartesian(xlim = c(0,10800)) +
theme_minimal()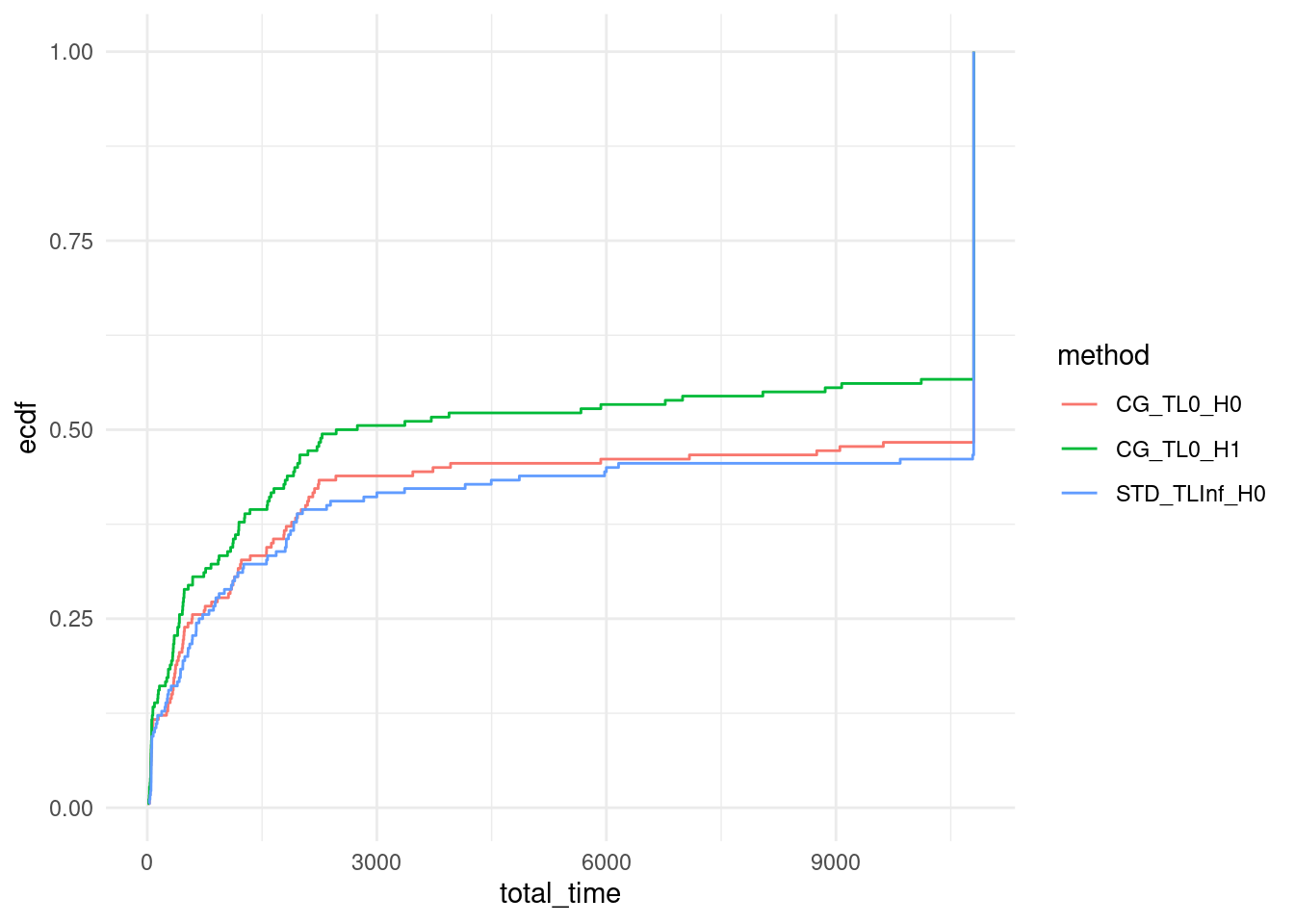
ggplot(data, aes(x = memory_used, col = method)) +
stat_ecdf(pad = FALSE) +
theme_minimal()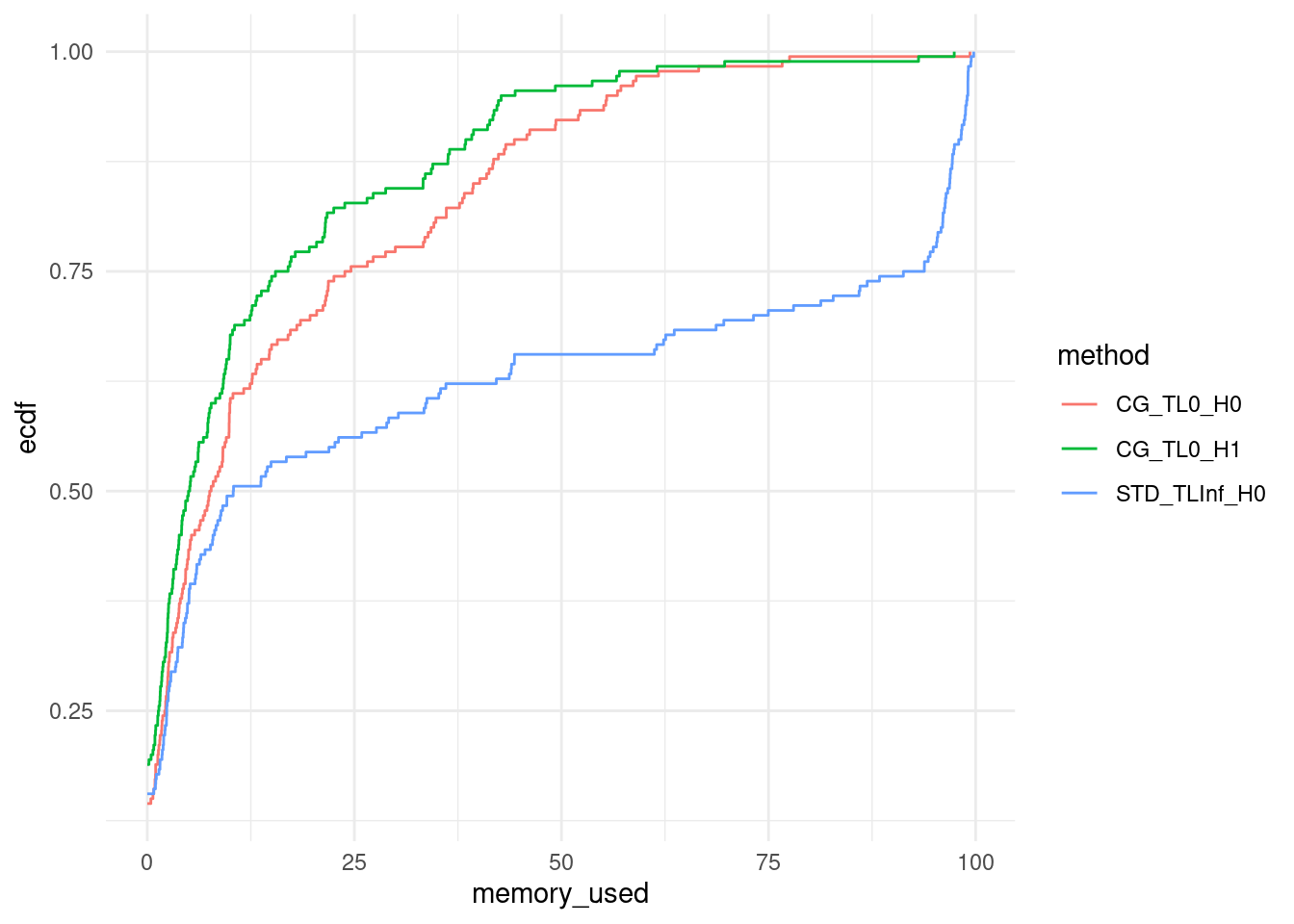
ggplot(data, aes(x = master_time / n_iterations, col = method)) + stat_ecdf(pad = FALSE) +
#coord_cartesian(xlim = c(0,10800)) +
theme_minimal()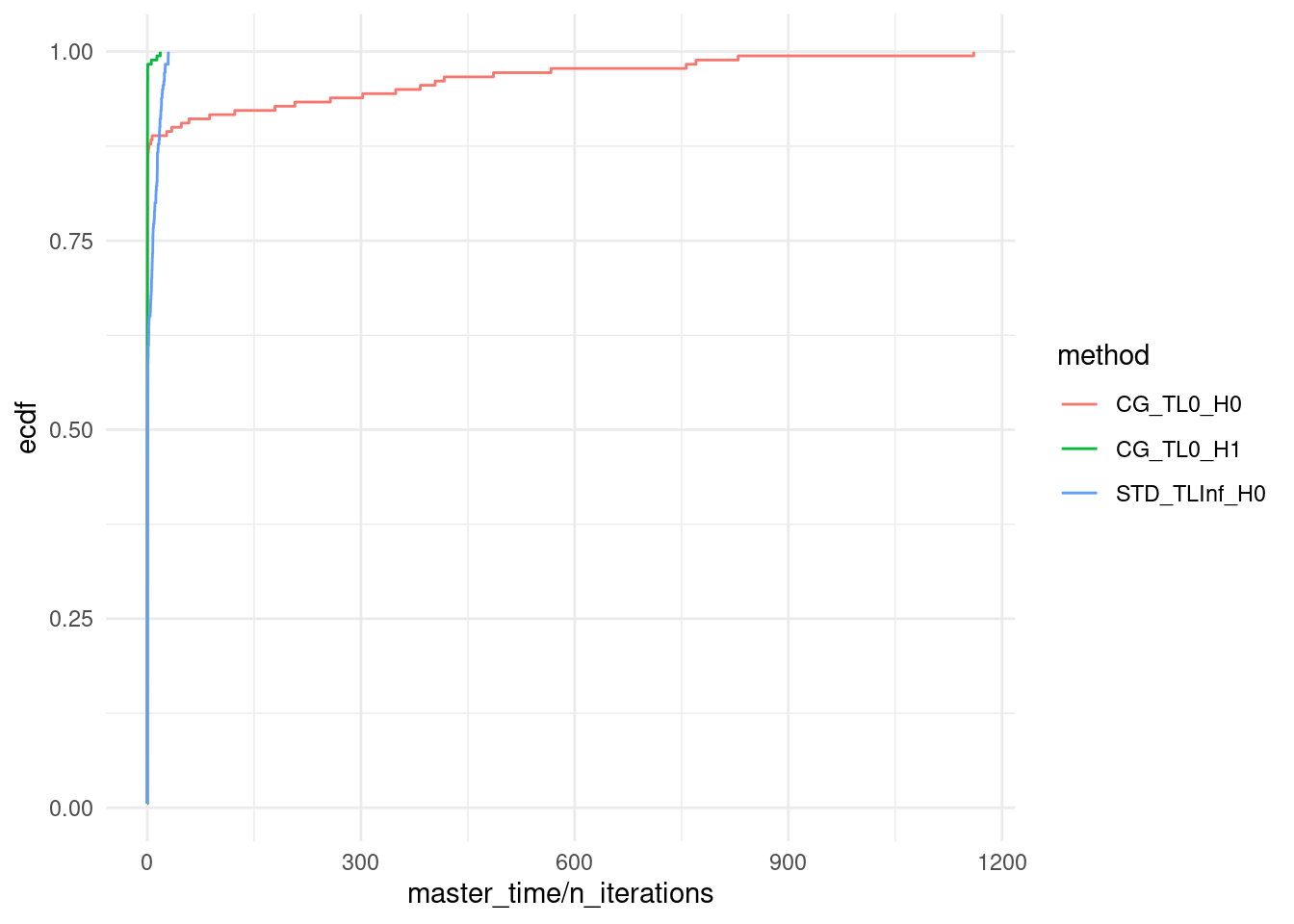
We export these results in csv to print them in tikz.
data_with_ecdf = data %>%
group_by(method) %>%
arrange(total_time) %>%
mutate(ecdf_value = ecdf(total_time)(total_time)) %>%
ungroup()
for (method in unique(data_with_ecdf$method)) {
output = data_with_ecdf[data_with_ecdf$method == method,]
output = output[,c("total_time", "ecdf_value")]
output$log_total_time = log10(output$total_time)
output = output[output$total_time < 10800,]
write.csv(output, file = paste0(method, ".csv"), row.names = FALSE)
}Summary table
In this section, we create a table summarizing the main outcome of our computational experiments.
We first focus on the solved instances.
summary_data_lt_10800 <- data %>%
filter(total_time < 10800) %>%
group_by(n_facilities, n_customers, Gamma, method) %>%
summarize(
avg_total_time = mean(total_time, na.rm = TRUE),
avg_master_time = mean(master_time, na.rm = TRUE),
avg_adversarial_time = mean(adversarial_time, na.rm = TRUE),
avg_n_iterations = mean(n_iterations, na.rm = TRUE),
sum_has_large_scaled = sum(has_large_scaled),
num_lines = n(),
.groups = "drop"
) %>%
ungroup() %>%
arrange(n_facilities, n_customers, Gamma, method)Then, we compute averages over the unsolved instances.
summary_data_ge_10800 <- data %>%
filter(total_time >= 10800) %>%
group_by(n_facilities, n_customers, Gamma, method) %>%
summarize(
avg_n_iterations_unsolved = mean(n_iterations, na.rm = TRUE),
num_lines_unsolved = n(),
.groups = "drop"
) %>%
ungroup() %>%
arrange(n_facilities, n_customers, Gamma, method)Finally, we merge our results.
transposed_data_lt_10800 <- summary_data_lt_10800 %>%
pivot_wider(names_from = method, values_from = avg_total_time:num_lines)
transposed_data_ge_10800 <- summary_data_ge_10800 %>%
pivot_wider(names_from = method, values_from = avg_n_iterations_unsolved:num_lines_unsolved) %>%
select(-n_facilities, -n_customers, -Gamma)
#cbind(
# transposed_data_lt_10800,
# transposed_data_ge_10800
#) %>%
# kable() %>%
# kable_styling(full_width = FALSE, position = "center")Second-stage Deviations
ggplot(data, aes(x = method, y = second_stage.std_dev / abs(second_stage.mean))) +
geom_boxplot() +
labs(title = "Boxplot of std.dev",
x = "Method",
y = "Number of Iterations") +
theme_minimal()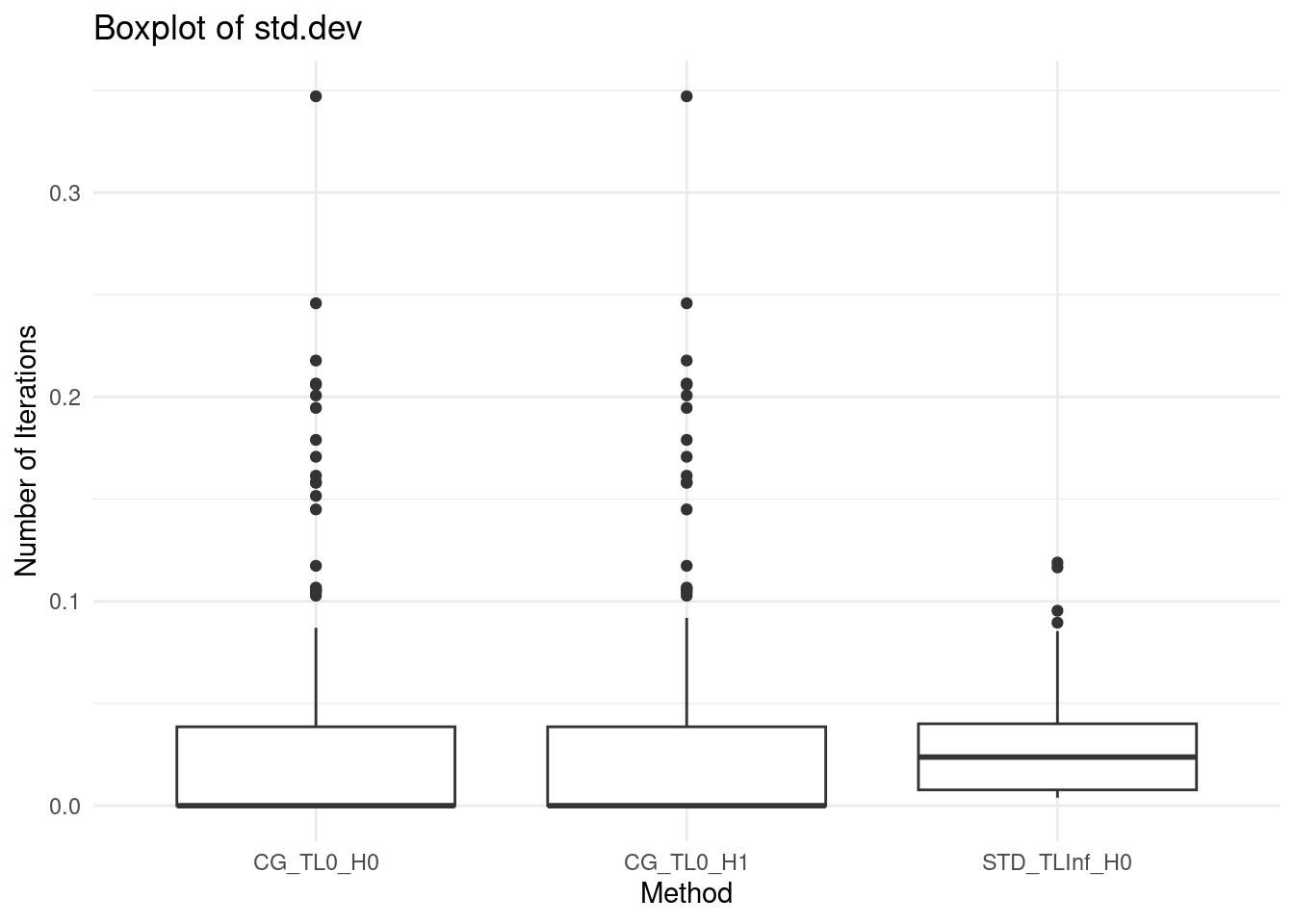
git push action on the public repository
hlefebvr/hlefebvr.github.io using rmarkdown and Github
Actions. This ensures the reproducibility of our data manipulation. The
last compilation was performed on the 20/01/26 18:19:45.
 Henri Lefebvre
Henri Lefebvre