Table of Contents
Computing Counterfactual Explanations for Linear Optimization: A New Class of Bilevel Models and a Tailored Penalty Alternating Direction Method > NETLIB
Loading Results
Instance Statistics
instances = read.csv("instances.csv", header = FALSE)
colnames(instances) = c("tag", "instance", "mps", "n_vars", "n_ctrs")
# Remove tag
instances$tag = NULL
# Clean instance name
instances$instance = sub("_.*", "", basename(instances$instance))
instances$mps = basename(instances$mps)
instances = instances[!duplicated(instances$instance), ]
paged_table(instances)Results
time_limit = 1800
data = rbind(
read.csv("new-results.csv", header = FALSE)
)
stats = c("time", "status", "reason", "objective", "n_outer_iterations", "n_inner_iterations","l1_norm", "l2_norm")
colnames(data) = c("tag", "instance", "n_vars", "n_ctrs", "desired_space_dim", "n_mutable_coefficients", "n_mutable_costs", "n_mutable_rhs", "method", "update_rule", "update_rule_parameter", "norm", "initial_penalty", "warm_start", "only_constraints", "sol_file", paste0("warm_start_", stats), stats, "solution_ok", "unconstrained_obj", "constrained_obj", "gap")
data$warm_start_status = ifelse(is.na(data$warm_start_status), "-", data$warm_start_status)
# Remove tag
data$tag = data$n_vars = data$n_ctrs = NULL
# Add a one-word solver description
data$solver = ifelse(data$method == "PADM", paste0(data$method, " - ", data$update_rule, " ", data$update_rule_parameter, " - ", data$norm, " - init ", data$initial_penalty, " - warm start ", data$warm_start, " - only constraints ", data$only_constraints), data$method)
# Add 'n_mutable_columns' based on instance name
data$n_mutable_columns = gsub(".*_(\\d+)$", "\\1", data$instance)
# Clean instance name
data$full_instance = basename(data$instance)
data$instance = sub("_.*", "", data$full_instance)
data$adjusted_time = ifelse(is.na(data$warm_start_time), 0, data$warm_start_time) + data$time
data = data %>% mutate(adjusted_time = ifelse(solution_ok == 0, time_limit, adjusted_time))
data$total_time = data$adjusted_time
data$solved = (data$status == "Optimal" | data$status == "Feasible") & data$adjusted_time < time_limit
n_unsolved = sum(!data$solved)
if (n_unsolved > 0) {
data[!data$solved,]$adjusted_time = time_limit
}
data$n_mutable_columns <- as.numeric(as.character(data$n_mutable_columns)) # Convert to numericMerge Instances and Results
data = merge(data, instances[, c("instance", "n_vars", "n_ctrs")],
by = "instance",
all.x = TRUE)data %>% filter(solution_ok == 0, method == "NLP-first", n_mutable_costs == 0) %>% select(instance, full_instance, n_mutable_coefficients, solution_ok, constrained_obj, unconstrained_obj, gap)## instance full_instance n_mutable_coefficients solution_ok constrained_obj
## 1 AFIRO AFIRO_0_10 15 0 -4.64646e+02
## 2 AFIRO AFIRO_9_10 13 0 -4.64532e+02
## 3 BRANDY BRANDY_18_10 127 0 1.12916e+03
## 4 CAPRI CAPRI_8_10 19 0 2.60699e+03
## 5 CAPRI CAPRI_11_10 49 0 2.72628e+03
## 6 LOTFI LOTFI_14_1 1 0 -2.52339e+01
## 7 LOTFI LOTFI_14_5 6 0 -2.52339e+01
## 8 MODSZK1 MODSZK1_16_1 1 0 7.33276e+02
## 9 PILOT PILOT_16_5 32 0 -5.57325e+02
## 10 PILOT PILOT_19_5 98 0 -5.57448e+02
## 11 PILOT PILOT_4_1 23 0 -5.57480e+02
## 12 PILOT-JA PILOT-JA_17_5 25 0 -6.11253e+03
## 13 PILOT-JA PILOT-JA_17_1 8 0 -6.11252e+03
## 14 PILOT-JA PILOT-JA_1_1 2 0 -6.13498e+03
## 15 PILOT-JA PILOT-JA_17_10 45 0 -6.11364e+03
## 16 SC105 SC105_18_10 11 0 -5.16070e+01
## 17 SC105 SC105_17_10 7 0 -5.18734e+01
## 18 SC205 SC205_10_1 1 0 -4.97182e+01
## 19 SC205 SC205_1_1 2 0 -5.22056e+01
## 20 SC205 SC205_10_10 1 0 -4.97182e+01
## 21 SC205 SC205_10_5 1 0 -4.97182e+01
## 22 SC205 SC205_1_5 2 0 -5.22056e+01
## 23 SC205 SC205_6_5 2 0 1.10813e-13
## 24 SC205 SC205_6_1 2 0 1.10813e-13
## 25 SC50A SC50A_10_10 8 0 -6.30426e+01
## 26 SC50A SC50A_1_10 11 0 -6.36179e+01
## 27 SC50A SC50A_15_5 5 0 -6.41937e+01
## 28 SC50A SC50A_15_10 9 0 -6.41937e+01
## 29 SC50A SC50A_19_5 4 0 0.00000e+00
## 30 SC50A SC50A_9_5 4 0 -6.41310e+01
## 31 SC50A SC50A_7_10 11 0 -6.28105e+01
## 32 SC50A SC50A_9_10 11 0 -6.41310e+01
## 33 SC50A SC50A_14_10 6 0 -4.61372e+01
## 34 SC50B SC50B_1_5 3 0 -6.83747e+01
## 35 SC50B SC50B_1_10 7 0 -6.83747e+01
## 36 SC50B SC50B_8_10 4 0 -6.85000e+01
## 37 SHARE1B SHARE1B_12_10 36 0 -7.65581e+04
## unconstrained_obj gap
## 1 -4.64753e+02 0.000231227
## 2 -4.64753e+02 0.000475658
## 3 1.12660e+03 0.002267640
## 4 2.60503e+03 0.000749901
## 5 2.72314e+03 0.001150530
## 6 -2.52647e+01 0.001222170
## 7 -2.52647e+01 0.001222170
## 8 7.28412e+02 0.006632540
## 9 -5.57408e+02 0.000148491
## 10 -5.57383e+02 0.000117095
## 11 -5.57384e+02 0.000172231
## 12 -6.11314e+03 0.000100030
## 13 -6.11314e+03 0.000100031
## 14 -6.15389e+03 0.003081550
## 15 -6.11428e+03 0.000104435
## 16 -5.22021e+01 0.011529900
## 17 -5.22021e+01 0.006335840
## 18 -4.97241e+01 0.000118196
## 19 -5.22158e+01 0.000196656
## 20 -4.97241e+01 0.000118196
## 21 -4.97241e+01 0.000118196
## 22 -5.22158e+01 0.000196656
## 23 0.00000e+00 0.001106910
## 24 0.00000e+00 0.001106910
## 25 -6.45751e+01 0.024308600
## 26 -6.45751e+01 0.015045200
## 27 -6.45751e+01 0.005940840
## 28 -6.45751e+01 0.005940840
## 29 1.29234e-13 0.001292340
## 30 -6.45751e+01 0.006925100
## 31 -6.45751e+01 0.028093800
## 32 -6.45751e+01 0.006925100
## 33 -6.45751e+01 0.399633000
## 34 -7.00000e+01 0.023769700
## 35 -7.00000e+01 0.023769700
## 36 -7.00000e+01 0.021897800
## 37 -7.65893e+04 0.000407670Performance Analysis
Summary à la Kurtz
This is the same table as Table 6 in “Counterfactual Explanations for Linear Optimization”, J. Kurtz (2024).
We focus on l1-norm with warm-start.
padm_with_warm_start = data %>%
filter(method == "PADM",
update_rule == "adapt",
norm == "l1",
initial_penalty == 5e2,
warm_start == 1)
var_bounds <- list(c(0, 534), c(534, 2167), c(2167, 22275))
ctr_bounds <- list(c(0, 351), c(351, 906), c(906, 16675))
labels <- c("small", "medium", "large")
summary_table = NULL
for (i in seq_along(labels)) {
for (j in seq_along(labels)) {
sub_summary_table <- padm_with_warm_start %>%
filter(
n_vars >= var_bounds[[i]][1] & n_vars <= var_bounds[[i]][2],
n_ctrs >= ctr_bounds[[j]][1] & n_ctrs <= ctr_bounds[[j]][2]
) %>%
mutate(
var_cat = labels[i],
ctr_cat = labels[j]
) %>%
group_by(var_cat, ctr_cat, n_mutable_columns) %>%
summarise(
`# inst.` = n_distinct(instance), # Count number of instances
`# full inst.` = n_distinct(full_instance),
`feasible (in %)` = sum(solved) / n_distinct(full_instance) * 100, # Percentage of feasible instances
`# mutable objective param.` = mean(n_mutable_costs, na.rm = TRUE), # Avg mutable objective parameters
`# mutable constraint param.` = mean(n_mutable_coefficients, na.rm = TRUE), # Avg mutable constraint parameters
.groups = "drop"
) %>%
arrange(var_cat, ctr_cat, n_mutable_columns) %>% # Sort by var_cat, ctr_cat, and n_mutable_columns
ungroup()
summary_table = rbind(summary_table, sub_summary_table)
}
}
summary_table %>%
kable("html", align = "c", col.names = c()) %>%
kable_styling(bootstrap_options = c("striped", "hover", "condensed"), full_width = FALSE, position = "center") %>%
add_header_above(c("n" = 1, "m" = 1, "# mut. columns" = 1, "# inst." = 1, "# full inst." = 1, "feasible (in %)" = 1,
"# mutable objective param." = 1, "# mutable constraint param." = 1)) %>%
group_rows("small", 1, 6) %>%
group_rows("medium", 7, 15) %>%
group_rows("large", 16, 24)| small | |||||||
| small | small | 1 | 28 | 560 | 18.928571 | 0.3017857 | 4.376786 |
| small | small | 5 | 28 | 560 | 24.642857 | 1.5535714 | 21.175000 |
| small | small | 10 | 28 | 560 | 33.214286 | 4.0607143 | 54.962500 |
| small | medium | 1 | 7 | 140 | 9.285714 | 0.7857143 | 5.085714 |
| small | medium | 5 | 7 | 140 | 12.142857 | 4.1071429 | 31.642857 |
| small | medium | 10 | 7 | 140 | 15.714286 | 10.8642857 | 79.628571 |
| medium | |||||||
| medium | small | 1 | 4 | 80 | 21.250000 | 0.6125000 | 5.925000 |
| medium | small | 5 | 4 | 80 | 21.250000 | 2.5875000 | 22.575000 |
| medium | small | 10 | 4 | 80 | 21.250000 | 6.7500000 | 54.125000 |
| medium | medium | 1 | 22 | 440 | 22.045455 | 0.4750000 | 10.420454 |
| medium | medium | 5 | 22 | 440 | 22.500000 | 2.4568182 | 19.011364 |
| medium | medium | 10 | 22 | 440 | 23.409091 | 6.3909091 | 35.563636 |
| medium | large | 1 | 8 | 160 | 16.250000 | 0.5312500 | 2.850000 |
| medium | large | 5 | 8 | 160 | 16.250000 | 2.0500000 | 10.675000 |
| medium | large | 10 | 8 | 160 | 16.250000 | 5.4500000 | 26.206250 |
| large | |||||||
| large | small | 1 | 2 | 40 | 0.000000 | 0.4250000 | 12.425000 |
| large | small | 5 | 2 | 40 | 0.000000 | 0.9250000 | 74.125000 |
| large | small | 10 | 2 | 40 | 0.000000 | 2.0250000 | 199.400000 |
| large | medium | 1 | 6 | 120 | 13.333333 | 0.5333333 | 2.250000 |
| large | medium | 5 | 6 | 120 | 13.333333 | 2.7583333 | 8.975000 |
| large | medium | 10 | 6 | 120 | 13.333333 | 7.3250000 | 22.016667 |
| large | large | 1 | 21 | 420 | 30.000000 | 0.5500000 | 5.126190 |
| large | large | 5 | 21 | 420 | 29.523809 | 2.3690476 | 20.792857 |
| large | large | 10 | 21 | 420 | 30.000000 | 6.0666667 | 53.085714 |
Solved Instances by Number of Mutable Columns
bar_data = padm_with_warm_start %>%
filter(solved == TRUE) %>% # Only consider solved instances
group_by(instance, n_mutable_columns) %>%
summarise(solved_count = n(), .groups = "drop") # Count solved instances
# Create bar plot
ggplot(bar_data, aes(x = instance, y = solved_count, fill = factor(n_mutable_columns))) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity", position = "dodge") + # Bar plot with bars side-by-side
coord_flip() +
labs(
title = "Number of Solved Instances by n_mutable_columns for Each Instance",
x = "Instance",
y = "Number of Solved Instances",
fill = "n_mutable_columns"
) +
theme_minimal() +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 90, hjust = 1), legend.position = "top") # Rotate x-axis labels for better readabilityComputational Times
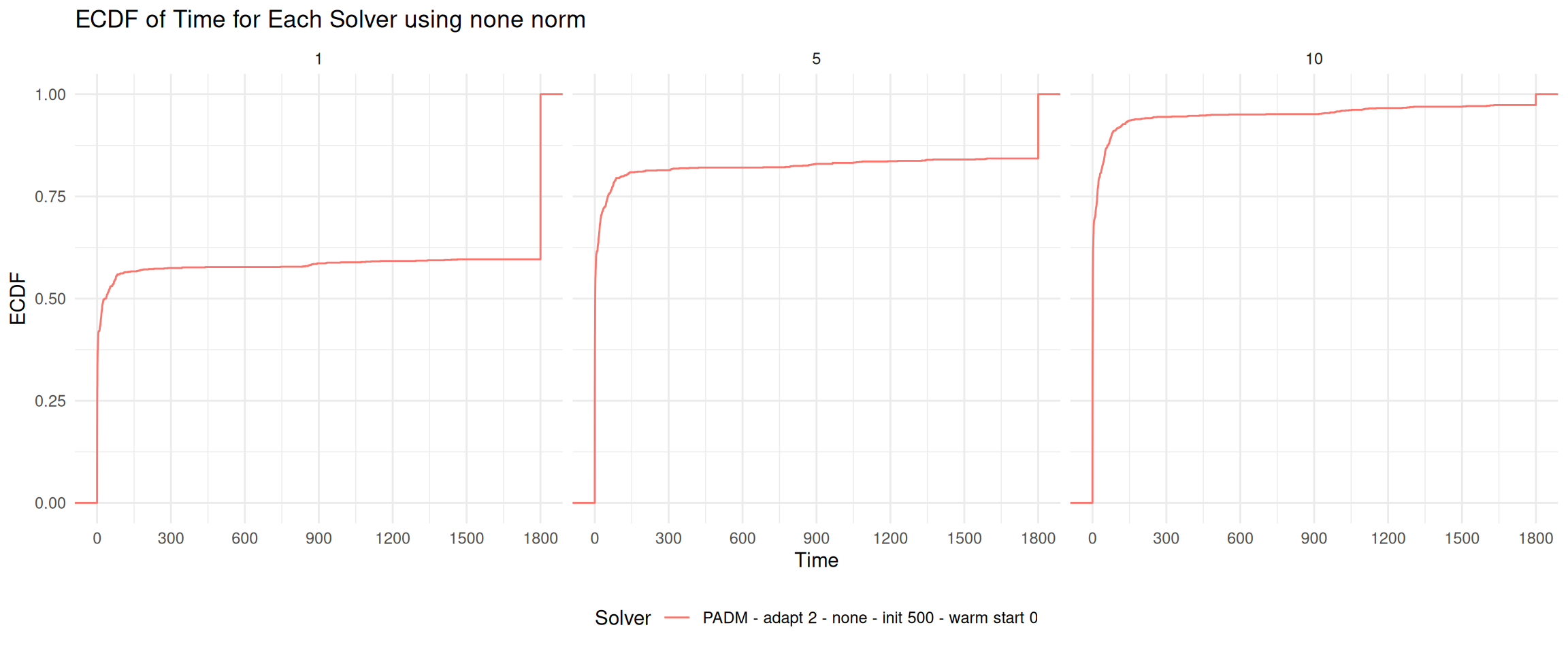
for (norm in unique(data$norm)) {
sub_data = data[data$norm == norm,]
sub_data = sub_data %>%
group_by( sub("^(.+_[0-9]+)_.*", "\\1", full_instance)) %>%
filter(any(solved == TRUE)) %>%
ungroup()
plot = ggplot(sub_data, aes(x = adjusted_time, group = solver, color = solver)) +
stat_ecdf(geom = "step") +
labs(title = paste0("ECDF of Time for Each Solver using ", norm, " norm"),
x = "Time",
y = "ECDF",
color = "Solver") +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "bottom") +
scale_x_continuous(breaks = seq(0, max(sub_data$adjusted_time), by = 300), limits = c(0, time_limit)) +
scale_y_continuous(breaks = seq(0, 1, by = 0.25)) +
facet_wrap(~ n_mutable_columns, ncol = 3) # Facet by mutable_columns, 3 columns
########## SAVING DATA TO FILE FOR TIKZ ##########
ecdf_data = data.frame(time = sub_data$adjusted_time)
for (n_mutable_columns_val in unique(sub_data$n_mutable_columns)) {
for (pair_val in unique(paste0(sub_data$method, "_", sub_data$warm_start))) {
parts = strsplit(pair_val, "_")[[1]]
method_val = parts[1]
warm_start_val = as.integer(parts[2])
facet_data = sub_data %>% filter(n_mutable_columns == n_mutable_columns_val & warm_start == warm_start_val & method == method_val)
ecdf_values = ecdf(facet_data$adjusted_time)(sub_data$adjusted_time)
ecdf_data = cbind(ecdf_data, y = ecdf_values)
colnames(ecdf_data)[ncol(ecdf_data)] = paste0(n_mutable_columns_val, "_", method_val, "_", warm_start_val)
}
}
ecdf_data <- as.data.frame(ecdf_data)
ecdf_data <- ecdf_data[order(ecdf_data$time), ]
ecdf_data = ecdf_data %>% filter(time < time_limit)
indices <- seq(1, length(ecdf_data$time), length.out = 100)
ecdf_data <- ecdf_data[indices, ]
file_name <- paste0("ecdf_", norm, ".csv")
write.csv(ecdf_data, file_name, row.names = FALSE)
###################################################
print(plot)
}
Solution Analysis
for (norm_val in unique(data$norm)) {
sub_data = data %>% filter(norm == norm_val)
sub_data = sub_data %>% mutate(l1_norm = ifelse(l1_norm < 1e-5, 1e-5, l1_norm))
sub_data = sub_data %>%
group_by(full_instance) %>%
filter(all(solved == TRUE)) %>%
ungroup()
summarize(sub_data)
plot = ggplot(sub_data, aes(x = l1_norm, y = as.factor(solver), fill = as.factor(solver))) +
geom_boxplot() +
labs(title = "Over those instances for which all methods computed a feasible point", #paste0("Boxplot of l1-norm of CE when using the objective function: ", norm),
x = "",
y = "") +
scale_y_discrete(labels = c("NLP", "NLP-first", "PADM", "PADM warm start")) +
scale_x_log10(breaks = scales::log_breaks(base = 10, n = 4)) +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "none", axis.text.y = element_text(angle = 90, hjust = .5)) # +
#facet_wrap(~ n_mutable_columns, ncol = 3)
print(plot)
#tikz(file = paste0("boxplot_", norm_val, ".tex"), width = 4, height = 3)
#print(plot)
#dev.off()
}
Infeasibility and Fails
gurobi_found = data %>%
filter(method == "NLP", status == "Optimal" | status == "Feasible") %>%
pull(full_instance)
gurobi_infeasible <- data %>%
filter(method == "NLP" & status == "Infeasible" & total_time < time_limit) %>%
pull(full_instance)
gurobi_unknown <- data %>%
filter(!(full_instance %in% gurobi_found) & !(full_instance %in% gurobi_infeasible)) %>%
pull(full_instance)The instance status is Feasible
feasible_instances = data %>%
filter(method == "PADM") %>%
filter(full_instance %in% gurobi_found) %>%
group_by(solver, status, reason) %>%
summarize(
Count = length(full_instance),
instances = paste0(paste0(unique(full_instance)[1:5], collapse = ", "), " ...")
)## `summarise()` has grouped output by 'solver', 'status'. You can override using
## the `.groups` argument.feasible_instances %>%
kable("html", booktabs = TRUE) %>%
kable_styling(full_width = FALSE) %>%
collapse_rows(columns = 1, valign = "top")| solver | status | reason | Count | instances |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PADM - adapt 2 - l1 - init 500 - warm start 0 - only constraints 0 | Fail | Cycling | 74 | AFIRO_13_10, AFIRO_0_10, AFIRO_13_5, AFIRO_9_10, BLEND_1_10 … |
| Feasible | Proved | 635 | 80BAU3B_18_10, 80BAU3B_17_10, 80BAU3B_15_10, 80BAU3B_4_10, 80BAU3B_7_10 … | |
| Infeasible | TimeLimit | 113 | AFIRO_6_10, AFIRO_3_10, BLEND_12_5, BLEND_8_10, BLEND_1_5 … | |
| PADM - adapt 2 - l1 - init 500 - warm start 1 - only constraints 0 | Fail | Cycling | 47 | AFIRO_13_10, AFIRO_13_5, BLEND_5_5, BLEND_16_10, BNL1_7_5 … |
| Feasible | Proved | 661 | 80BAU3B_0_5, 80BAU3B_5_10, 80BAU3B_15_10, 80BAU3B_5_5, 80BAU3B_17_10 … | |
| Infeasible | TimeLimit | 114 | AFIRO_3_10, BLEND_10_5, BLEND_16_5, BLEND_17_5, BLEND_8_1 … |
The instance status is Infeasible
infeasible_instances = data %>%
filter(method == "PADM") %>%
filter(full_instance %in% gurobi_infeasible) %>%
group_by(solver, status, reason) %>%
summarize(
Count = length(full_instance),
instances = paste0(paste0(unique(full_instance)[1:5], collapse = ", "), " ...")
)## `summarise()` has grouped output by 'solver', 'status'. You can override using
## the `.groups` argument.infeasible_instances %>%
kable("html", booktabs = TRUE) %>%
kable_styling(full_width = FALSE) %>%
collapse_rows(columns = 1, valign = "top")| solver | status | reason | Count | instances |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PADM - adapt 2 - l1 - init 500 - warm start 0 - only constraints 0 | Fail | Cycling | 908 | 25FV47_19_10, 80BAU3B_11_10, 80BAU3B_11_5, 80BAU3B_11_1, ADLITTLE_16_1 … |
| Feasible | Proved | 290 | 25FV47_8_1, 25FV47_10_1, 25FV47_6_1, 25FV47_14_1, 25FV47_2_1 … | |
| Infeasible | TimeLimit | 2065 | 25FV47_19_1, 25FV47_9_10, 25FV47_4_1, 25FV47_19_5, 25FV47_9_5 … | |
| Unbounded | Proved | 2 | GROW15_19_1, GROW15_5_1, NA, NA, NA … | |
| PADM - adapt 2 - l1 - init 500 - warm start 1 - only constraints 0 | Fail | Cycling | 587 | 80BAU3B_11_5, 80BAU3B_11_1, ADLITTLE_1_1, ADLITTLE_2_1, ADLITTLE_12_1 … |
| Feasible | Proved | 292 | 25FV47_16_1, 25FV47_14_1, 25FV47_1_1, 25FV47_10_1, 25FV47_6_1 … | |
| Infeasible | TimeLimit | 2385 | 25FV47_9_5, 25FV47_4_1, 25FV47_19_10, 25FV47_19_1, 25FV47_9_1 … | |
| Unbounded | Proved | 1 | GROW15_19_1, NA, NA, NA, NA … |
The instance status is Unknown
unknown_instances = data %>%
filter(method == "PADM") %>%
filter(full_instance %in% gurobi_unknown) %>%
group_by(solver, status, reason) %>%
summarize(
Count = length(full_instance),
instances = paste0(paste0(unique(full_instance)[1:5], collapse = ", "), " ...")
)## `summarise()` has grouped output by 'solver', 'status'. You can override using
## the `.groups` argument.unknown_instances %>%
kable("html", booktabs = TRUE) %>%
kable_styling(full_width = FALSE) %>%
collapse_rows(columns = 1, valign = "top")| solver | status | reason | Count | instances |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PADM - adapt 2 - l1 - init 500 - warm start 0 - only constraints 0 | Fail | Cycling | 127 | ADLITTLE_10_5, ADLITTLE_6_1, ADLITTLE_9_1, ADLITTLE_1_5, ADLITTLE_9_5 … |
| Feasible | Proved | 665 | 25FV47_16_5, 25FV47_0_5, 25FV47_3_10, 25FV47_16_10, 25FV47_12_10 … | |
| Infeasible | TimeLimit | 869 | 25FV47_17_10, 25FV47_18_1, 25FV47_17_5, 25FV47_3_1, 25FV47_18_10 … | |
| Unbounded | Proved | 12 | GROW15_5_10, GROW15_5_5, GROW15_19_10, GROW15_19_5, GROW15_8_1 … | |
| PADM - adapt 2 - l1 - init 500 - warm start 1 - only constraints 0 | Fail | Cycling | 70 | ADLITTLE_19_5, ADLITTLE_6_1, ADLITTLE_1_5, ADLITTLE_19_1, ADLITTLE_12_10 … |
| Feasible | Proved | 692 | 25FV47_16_10, 25FV47_2_10, 25FV47_16_5, 25FV47_3_10, 25FV47_12_5 … | |
| Infeasible | TimeLimit | 906 | 25FV47_17_10, 25FV47_17_5, 25FV47_18_1, 25FV47_18_5, 25FV47_3_1 … | |
| Unbounded | Proved | 5 | GROW15_5_10, GROW22_15_1, GROW22_10_5, GROW22_15_5, GROW22_10_1 … |
ws_gap = data %>%
filter(method == "PADM", !is.na(warm_start_l1_norm), !is.na(l1_norm)) %>%
mutate(gap_warm_start = (warm_start_l1_norm - l1_norm) / (1e-10 + warm_start_l1_norm)) %>%
select(full_instance, n_mutable_columns, warm_start_l1_norm, l1_norm, gap_warm_start)
ws_gap %>% filter(gap_warm_start < 0)## full_instance n_mutable_columns warm_start_l1_norm l1_norm gap_warm_start
## 1 ADLITTLE_3_1 1 1.03572e-06 2.07144e-06 -0.9999035
## 2 GANGES_0_1 1 4.59788e-07 1.23802e-06 -1.6922207ggplot(ws_gap, aes(x = gap_warm_start)) +
stat_ecdf(geom = "step")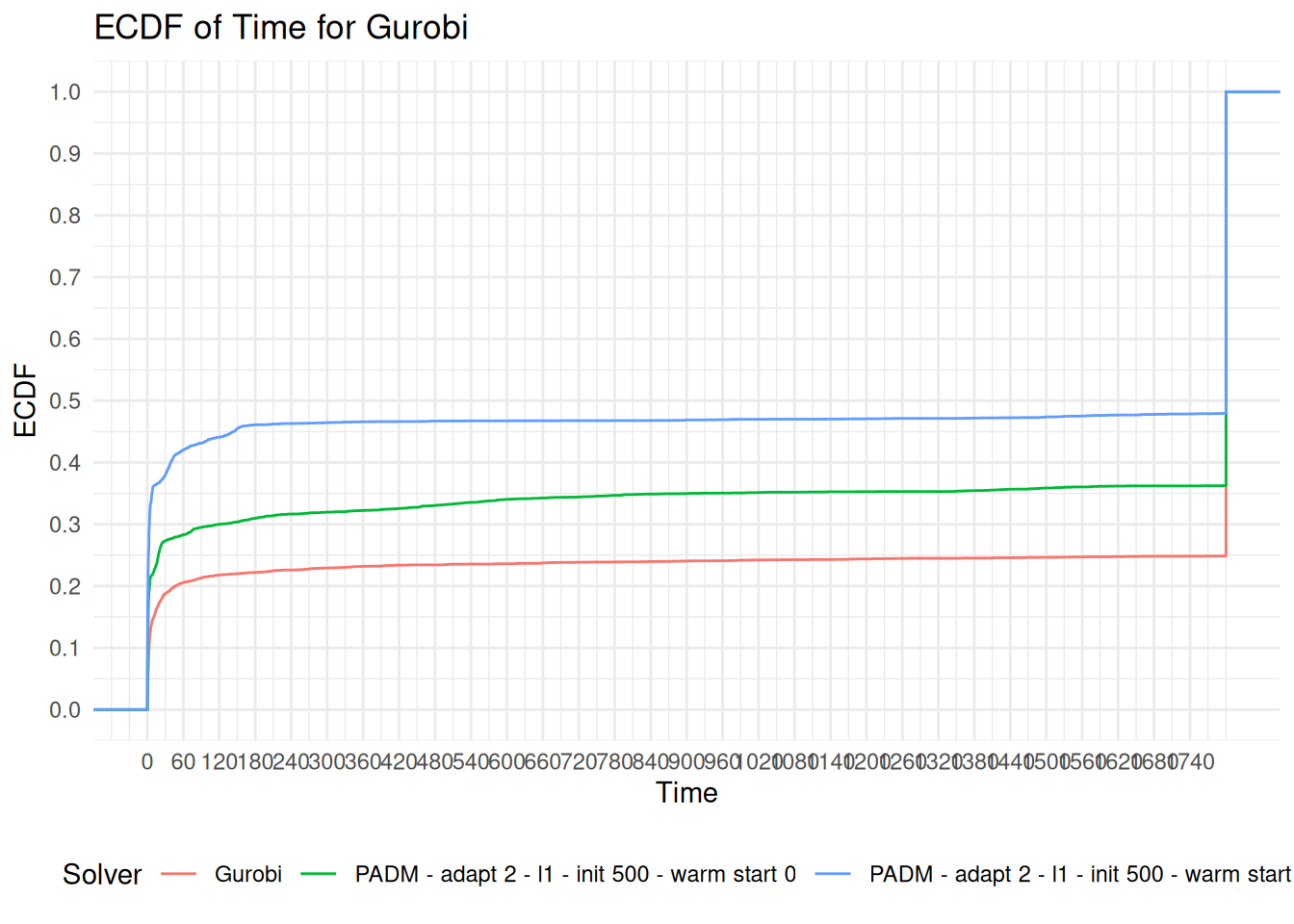
x = seq(-1,1,.01)
ecdf_ws_improve = data.frame(
p = x,
ecdf = ecdf(ws_gap$gap_warm_start)(x)
)
write.csv(ecdf_ws_improve, file = "ecdf_ws_improve.csv", row.names = FALSE)
This document is automatically generated after every
git push action on the public repository
hlefebvr/hlefebvr.github.io using rmarkdown and Github
Actions. This ensures the reproducibility of our data manipulation. The
last compilation was performed on the 20/01/26 18:19:24.
 Henri Lefebvre
Henri Lefebvre